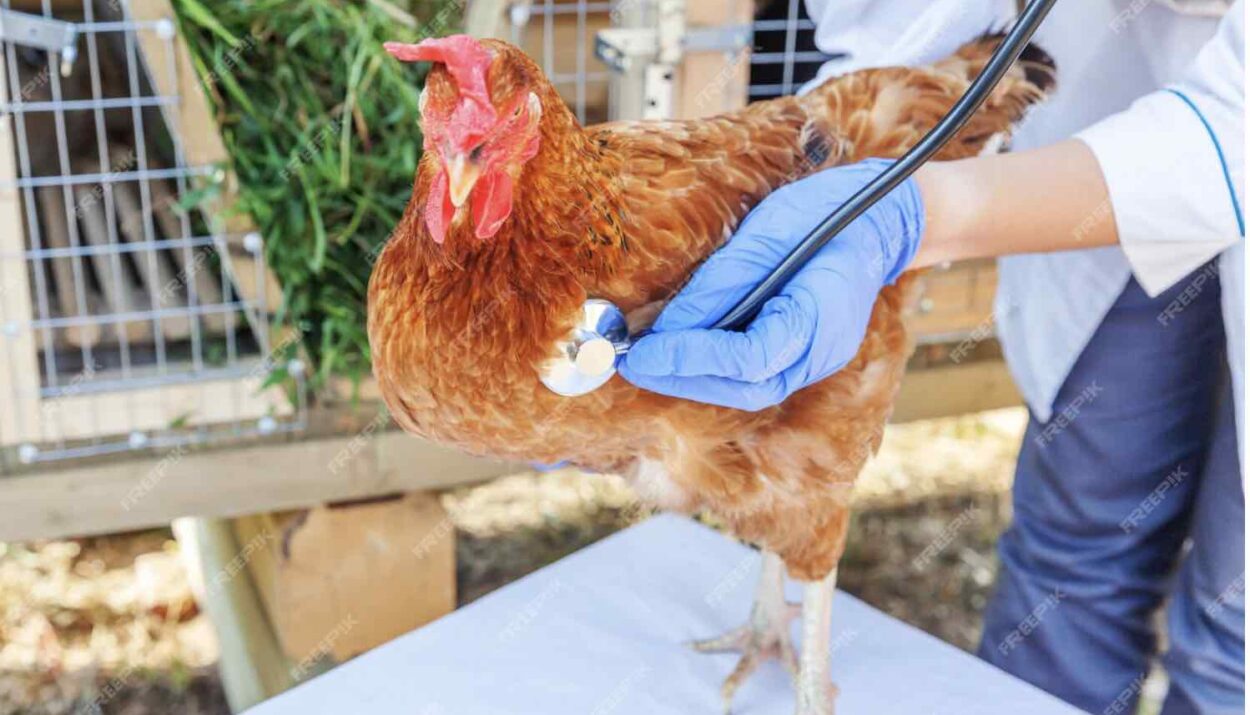
A woman in Wyoming has been hospitalized with H5N1 bird flu, marking the first recorded human case in the state and the latest in a growing series of infections across the United States.
According to the Wyoming Department of Health, the patient is an older adult with preexisting health conditions that may have made her more vulnerable to the virus. She is currently receiving treatment out of state.
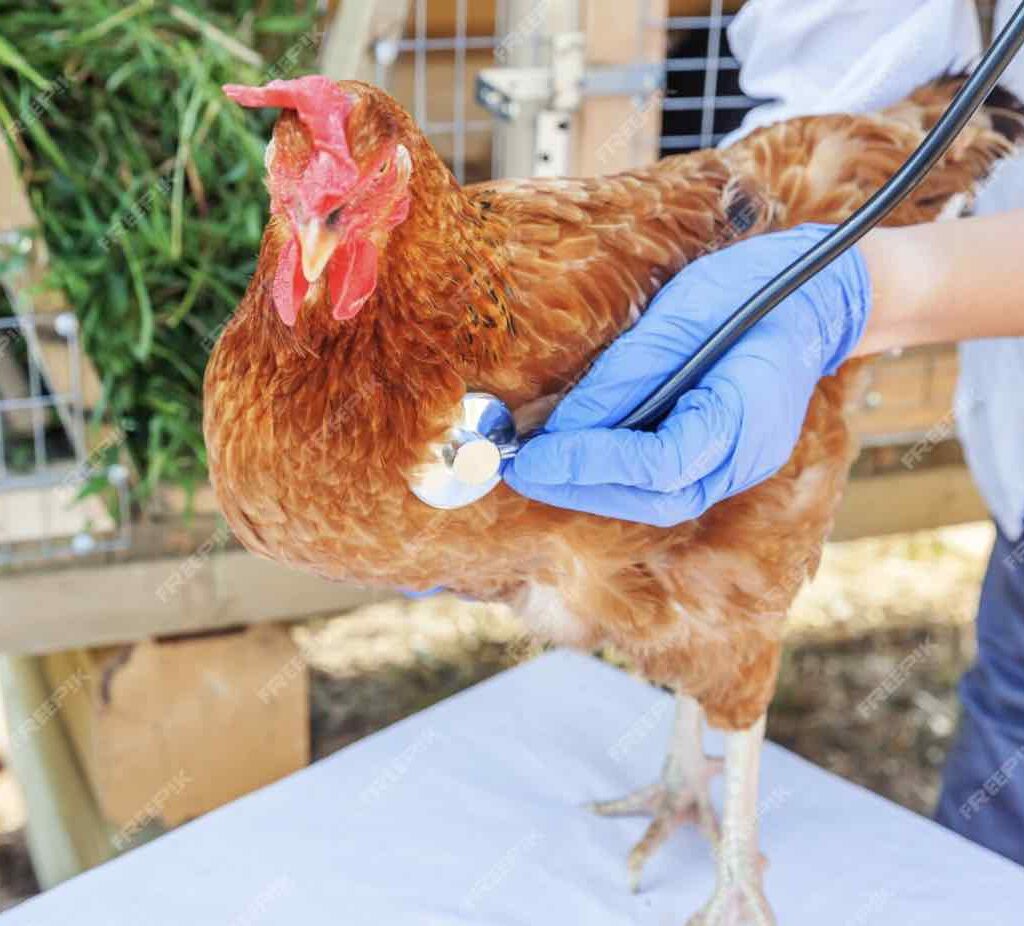

This case brings the total number of human H5N1 infections in the U.S. to 70 since 2024, though the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has yet to update its official count. The woman is the fourth person in North America to be hospitalized due to the disease.
Previously, a case in Louisiana resulted in a fatality.
Growing Concerns Amid Widespread Outbreaks
The source of the woman’s infection is believed to be direct contact with sick birds from a backyard flock. Health officials have not yet determined whether she contracted the D1.1 strain, which is prevalent in wild birds, poultry, and cattle in states like Nevada and Arizona, or the B3.13 strain, which has primarily affected dairy herds.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) reports that 968 dairy herds across 16 states have been infected, with a recent case confirmed in Arizona. H5N1 has also been detected in wild birds and commercial poultry operations throughout Wyoming.
Despite the increasing cases, Dr. Alexia Harrist, Wyoming’s state health officer and epidemiologist, emphasized that the risk to the general public remains low. “While this is a significant development as bird flu activity is monitored in Wyoming and across the country, it is not something we believe requires a high level of concern among most Wyoming residents,” she stated.
Preventative Measures and Public Health Guidelines
The CDC and Wyoming health officials have reiterated key safety measures to minimize the risk of infection:
- Avoid direct contact with wild birds and sick or dead poultry.
- Do not consume raw or undercooked eggs, meat, or other animal products.
- Refrain from drinking raw milk or consuming dairy products made from unpasteurized milk.
There is currently no evidence of human-to-human transmission of H5N1, reinforcing the belief that the virus remains primarily an animal health concern. However, health authorities continue to monitor outbreaks closely as the virus spreads among livestock and wildlife populations.
For further updates and expert insights, stay connected with My Unbounded Life.
Sources:
- Wyoming Department of Health
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA)

Play Sky Jumper!
Test your reflexes in Sky Jumper! How far can you go? Click below to play now.
Play Now